135. 网络编程
概述
地球村:现代科技缩小世界的时空距离
信件 ——> 网络编程
计算机网络
计算机网络是指将
地理位置不同的具有独立功能的多台计算机机器外部设备,通过通信线路连接起来,在网络操作系统,网络管理软件及光网络通信协议(类似于方言、语言)的管理和协调下,实现资源共享和信息传递的计算机系统。
网络编程的目的
无线电台… :传播交流信息,数据交换。(通信)
想要达到这个效果需要什么
- 如何准确的定位网络上的一台主机 :
192.168.16.124:port,定位到这个计算机上的某个资源 - 找到了这个主机,如何传输数据呢?
javaweb: 网页编程B/S架构
网络编程:TCP/IP
网络通信的要素
如何实现网络的通信?
通信双方的地址:
ip(唯一(指的是公网,不是局域网))port192.168.16.124:5900(ip:port):就可以定位到某台计算机上的某一个应用
规则:网络通信的协议
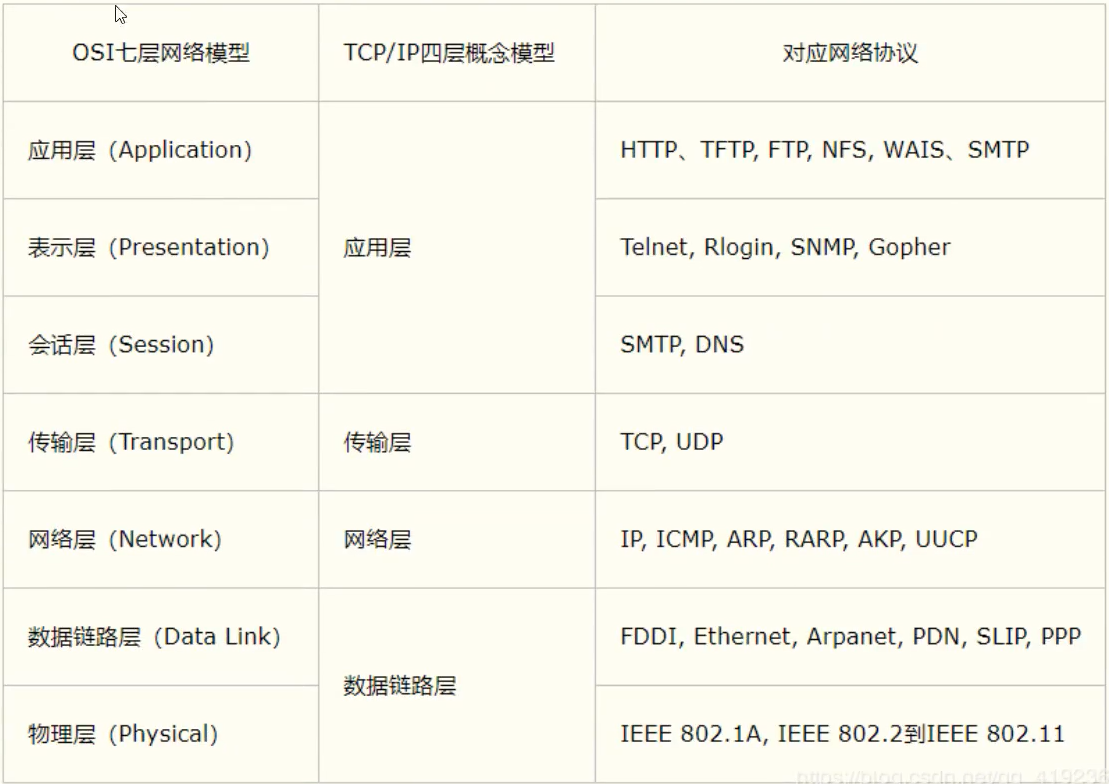
http, ftp, smtp, tcp, udp, ….
TCP/IP参考模型:
本章目的:

小结
- 网络编程中有两个主要的问题
- 如何准确的定位网络上的一台或多台主机
- 找到主机之后如何进行通信
- 网络编程中的要素
IP和port:ip- 网络通信协议:
udp,tcp
- 万物皆对象
IP
ip地址:InetAddress
用处:
- 唯一定位一台网络上计算机
127.0.0.1(localhost): 本机ip地址的分类IP地址分类:IPV4/IPV6IPV4: 如127.0.0.1。4个字节(32位)组成(0-255),全球42亿个(30亿都在北美,亚洲4亿,2011年就用尽了)IPV6: 如2001:0bb2:aaaa:0015:0000:00000:1aaa:1312。16字节(128位)组成,8个无符号整数(4个字节),用的是16进制(16进制占4位)。
- 公网(互联网使用)和私网(局域网使用)
192.168.xx.xx:局域网,专门给组织内部使用ABCD类地址
- 域名:记忆
IP问题IP:www.vip.com
端口
端口表示计算机上的一个程序的进程(类似于:一栋楼代表一个 ip,门牌号代表 端口)
不同的进程有不同的端口号,用来区分软件
被规定:
0~65535TCP/UDP端口:65535 * 2,单个协议下端口号不能冲突,不同协议下,端口可以冲突端口分类
公有端口:(0~1023)最好不要用
HTTP: 80HTTPS:43FTP:21SSH:22Telent: 23
程序注册端口:1024~49151,分配给用户或者程序,建议不要用
Tomcat: 8080Mysql:3306Oracle: 1521
动态、私有:49152~65535,建议不要用
Idea:63342查看所有接口
1
2
3netstat -ano # 查看所有端口
netstat -ano|findstr "5900"# 管道流: |,查看指定的端口
tasklist|findstr "8696" # 查看指定端口的进程打开任务管理器:
ctrl+shift+esc
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25package com.kuangstudy.net.module4;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* @author Qeuroal
* @date 2021-03-21 16:15
* @description
* @since
*/
public class TestInetSocketAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080);
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress);
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress2 = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080);
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress2);
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getAddress());
// 地址,可以更改hosts文件来更改映射
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getHostName());
// 端口
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getPort());
}
}图片
![image-20210321162748752]()
通信协议
- 协议: 约定,就好比我们现在说的普通话
- 网络通信协议:针对于网络所产生的协议,如:速率,传输码率,代码结构,传输控制……
- 问题:非常的复杂
- 大事化小:分层
- TCP/IP协议簇:实际上是一组协议,不止两个协议。
重要的协议:
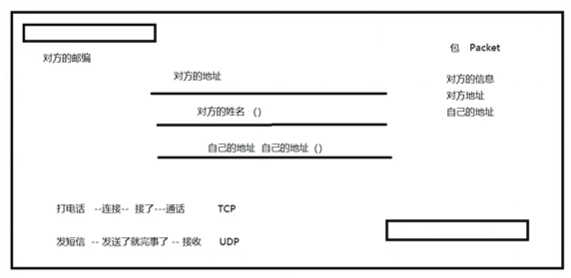
TCP: 用户传输协议,类似于打电话UDP: 用户数据报协议,类似于发短信
出名的协议:
TCP: 用户传输协议IP:网络互连协议![image-20210321163837855]()
TCP, UDP对比
TCP: 打电话连接:稳定
连接:三次握手,四次挥手
三次握手:
最少需要三次,保证稳定连接!
A:你瞅啥?
B:瞅你咋地?
A:干一场!
四次挥手
A:我要走了!
B:你真的要走了吗!
B:你真的真的要走了吗?
A:我真的要走了!
客户端、服务端连接
传输完成,释放连接,效率低
UDP: 发短信- 不连接:不稳定
- 客户端、服务端连接:没有明确的界限
- 不管有没有准备好,都可以发给你
- 类似于导弹攻击
DDOS: 洪水攻击(饱和攻击)
TCP
客户端
- 连接服务器
socket - 发送消息
1 | package com.kuangstudy.net.module6; |
服务器
- 建立服务的端口
ServerSocket - 等待用户的连接
accept - 接受用户消息
1 | package com.kuangstudy.net.module6; |
文件上传
读取文件->流->传出去
服务器端
1 | package com.kuangstudy.net.module7; |
客户端
1 | package com.kuangstudy.net.module7; |
Tomcat
服务端
- 自定义 S
- Tomcat服务器 S: Java后台开发!
客户端
- 自定义 S
- 浏览器 B
UDP
发短信:不用连接,需要知道对方的地址
涉及到两个类:
DatagramPacketDatagramSocket
发送端
1 | package com.kuangstudy.net.module9; |
接收端
1 | package com.kuangstudy.net.module9; |
本质上没有服务器:因为可以互相发送,因此就没有服务器的概念
咨询
类似于:广告的客服
xxx: 你好
xxx: 你好
BufferedReader: 包装流包装System.in,为了控制台读取1
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in))
循环发送消息
1 |
循环接收消息
1 |
在线咨询
两个人都是发送方,同时也都是接收方
TalkSend
1 |
TalkReceive
1 |
TalkStudent
1 |
TalkTeacher
1 |
URL
如:
https://www.baidu.com/统一资源定位符:定位资源的,定位互联网上的某一个资源
DNS域名解析: 将www.baidu.com==>xxx.xx.xx.xx组成(可以少,但不能多)
URL(): 网络类,代表一个地址param:Stringurl.getProtocol: 得到协议名url.getHost(): 得到主机ipurl.getPort(): 得到端口url.getPath(): 文件地址url.getFile(): 得到文件全路径url.getQuery: 得到参数(如:查询的名字)url.openConnection(): 打开连接urlConnection.getInputStream(): 得到流urlConnection.disconnect(): 断开连接
下载文件
- 下载地址
- 连接到这个资源,用
HTTP连接 - 下载
getResource
getResource读取的是 out 下的文件,即 classpath
- 相对路径: 即在当前包内的路径,如:
Test.class.getResource("xly2.png");,xly2.png在当前包内,或者说和运行的class在同一目录下 - 绝对路径: 用
/表示,代表是当前项目下,如Test.class.getResource("/resource/xly2.png"),如上图可见resource的位置
new File
读取的是 目录文件,如下所示
1 | new FileInputStream(new File("src/resource/xly2.png")); |

